Gingivitis is one of the most common gum problems, yet it is often ignored because it may not cause severe pain in the early stages. Many people notice bleeding gums while brushing and assume it is normal, but this is usually the first warning sign of gingivitis. If left untreated, it can progress into more serious gum disease and even lead to tooth loss. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options can help protect your oral and overall health.
What Is Gingivitis?
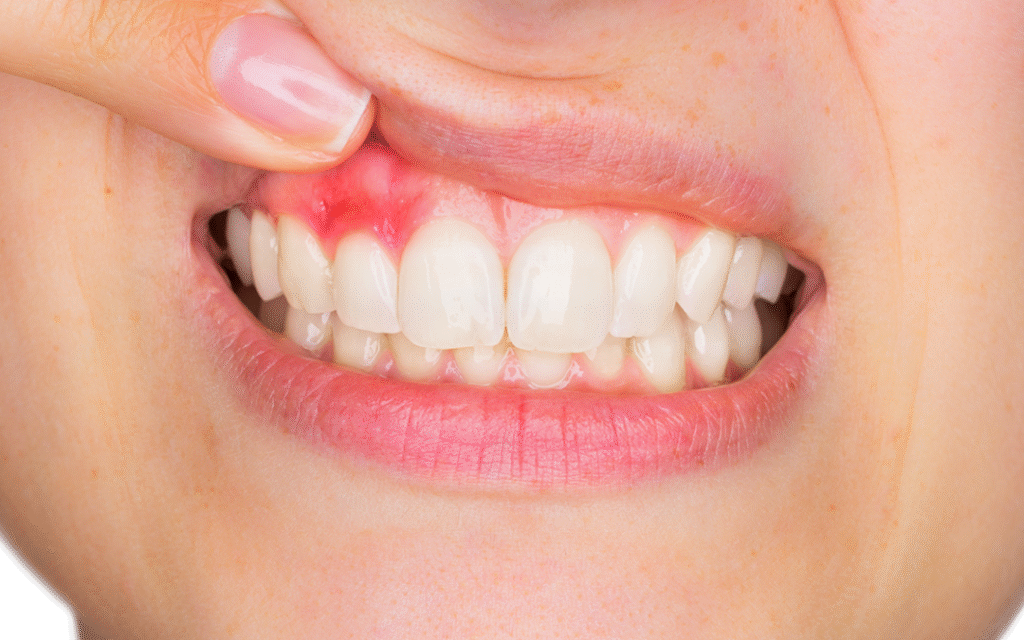
Gingivitis is a mild and early form of gum disease that affects the soft tissues surrounding the teeth. It occurs when plaque—a sticky layer of bacteria—builds up on teeth and irritates the gums. This irritation leads to inflammation, redness, and swelling of the gum tissue. The good news is that gingivitis is reversible if treated on time.
Unlike advanced gum disease, gingivitis does not damage the bone or tissues that support the teeth. However, ignoring it can allow the condition to worsen, turning into periodontitis, which is far more difficult to treat. Regular dental care and good oral hygiene play a crucial role in preventing this condition.
Common Symptoms of Gingivitis
The symptoms of gingivitis may be subtle at first, which is why many people overlook them. One of the most noticeable signs is bleeding gums, especially while brushing or flossing. Healthy gums do not bleed, so this symptom should never be ignored. Other common signs include red, swollen, or tender gums that may feel sore when touched.
Bad breath that does not go away even after brushing is another symptom of gingivitis. Some people may also notice gums pulling away slightly from the teeth or a shiny appearance of the gums. Pain is usually mild or absent, which makes early detection challenging. Paying attention to these warning signs can help prevent further complications.
What Causes Gingivitis?
The primary cause of gingivitis is poor oral hygiene, which allows plaque to build up on the teeth and gums. When plaque is not removed through brushing and flossing, it hardens into tartar, which can only be removed by a dentist. This buildup creates an environment where bacteria thrive and irritate the gums.
Other contributing factors include smoking, hormonal changes during pregnancy, uncontrolled diabetes, certain medications, and nutritional deficiencies—especially a lack of vitamin C. Stress and weakened immunity can also make gums more vulnerable to infection. Understanding these causes helps in adopting better preventive habits.
How Gingivitis Is Diagnosed
Dentists usually diagnose gingivitis during a routine dental examination. They look for signs such as redness, swelling, bleeding, and plaque or tartar buildup around the gum line. In most cases, X-rays are not required because gingivitis does not affect the bone structure.
However, a dentist may still recommend X-rays to rule out more advanced gum disease if symptoms appear severe. Early diagnosis is key because treatment at this stage is simple, effective, and less expensive. Regular dental checkups make it easier to detect gingivitis before it progresses.
Effective Treatment Options for Gingivitis
Treating gingivitis focuses on removing plaque and tartar and improving oral hygiene habits. Professional dental cleaning is often the first and most important step. During this procedure, the dentist removes hardened tartar from above and below the gum line, allowing the gums to heal.
At home, brushing twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and flossing daily are essential. Dentists may also recommend antiseptic mouthwashes to reduce bacteria. In some cases, lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking and managing underlying health conditions are necessary. With consistent care, symptoms usually improve within a few weeks.
Home Care Tips to Prevent Gingivitis
Preventing gingivitis is largely about maintaining good daily oral hygiene. Brushing gently but thoroughly at least twice a day helps remove plaque before it hardens. Using a soft-bristled toothbrush and replacing it every three months is also important for effective cleaning.
Flossing daily removes food particles and plaque from areas that a toothbrush cannot reach. A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports gum health, while limiting sugary foods reduces bacterial growth. Regular dental visits ensure that any early signs of gum disease are treated promptly.
Book Appointment with Best Dentist in Islamabad via InstaCare
If you are experiencing symptoms like bleeding gums, persistent bad breath, or gum swelling, it is important to consult a dentist without delay. Early treatment can reverse gingivitis and prevent serious dental complications in the future. Delaying care may lead to advanced gum disease, which can affect both oral and overall health.
You can easily book an appointment with the best dentist in Islamabad via InstaCare, where you can find experienced dental professionals, compare profiles, and choose a time that suits your schedule. Taking this simple step today can protect your smile for years to come.
Conclusion
Gingivitis is a common but preventable and reversible gum condition. Many people ignore its early signs, assuming they are harmless, but untreated gingivitis can lead to serious dental problems. The key lies in early detection, proper oral hygiene, and regular dental checkups.
By understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options, you can take control of your gum health. Simple habits like brushing, flossing, and timely dental visits can make a significant difference. Healthy gums not only support strong teeth but also contribute to overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Is gingivitis painful?
Gingivitis is usually not painful in its early stages. Most people notice bleeding, redness, or swelling rather than pain, which is why it often goes unnoticed.
- Can gingivitis go away on its own?
No, gingivitis does not go away without proper oral care. However, it can be completely reversed with professional dental cleaning and good oral hygiene.
- How long does it take to treat gingivitis?
With proper treatment and daily care, gingivitis usually improves within one to two weeks. Consistency is key to full recovery.
- Does gingivitis cause bad breath?
Yes, persistent bad breath is a common symptom because bacteria build up around the gums when plaque is not removed properly.
- When should I see a dentist for gingivitis?
You should see a dentist as soon as you notice bleeding gums, swelling, or ongoing bad breath. Early treatment prevents more serious gum disease.